This website uses cookies for a better browsing experience.
If you agree to the use of cookies, please click the "Agree" button.
Please refer to the Privacy Policy regarding the use of cookies on this site.
Features
- Can satisfy the requirements for stable performance of bearings by supporting loads and allowing elongation and rotational absorption over a long period of time.
- Customizable dispersion ratio of horizontal force during an earthquake will allow the bridge design to be more reasonable.
- Maintenance is easier compared with steel bearings.
- Simpler structure provides with ease of replacement work.
- LRB performance can be flexibly designed according to the size and the characteristics of the structure by adjusting the size of the lead plug.

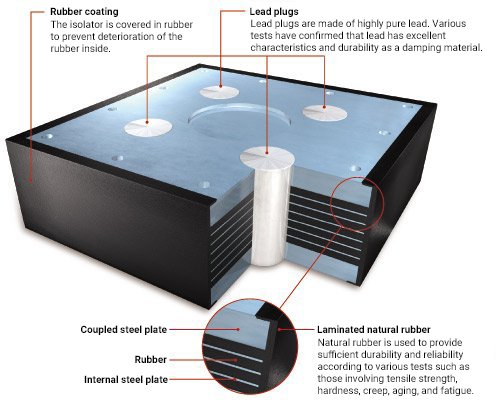
Structure
Cure adhesion laminated rubber bearing with alternately piled up rubber and steel plate.
*The specifications are subject to change for improvement without prior notice.
Basic Characteristics of the LRB (Laminated Rubber)
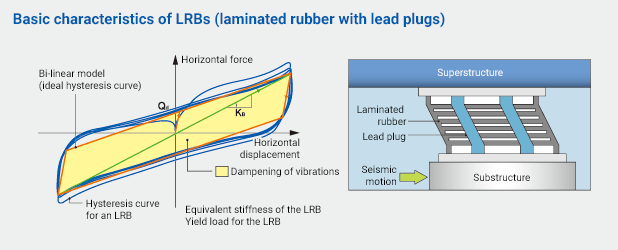
The Function of Laminated Rubber/ Lead Plug
The Function of Laminated Rubber
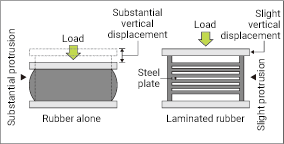
- 1. The steel plate reinforced rubber will firmly support the structure. (Load supporting and rotational absorption function)
High rigidity in the vertical direction as compared to the single rubber provides with the stable support of the structure.
- Transform the seismic vibration into a slow movement. (Horizontal Elasticity Function)
Softness in the horizontal direction will calm down the severe seismic vibration and make it a long-period vibration of the structure.
- 3. Returns the structure to the original position (Restoration function)
The restoration force of the rubber will return the structure to the original position after the earthquake terminated.
The Function of Lead Plug
- 4. Damps the severe vibration of structure. (Vibration damping function)
The Lead Plug will be plastically deformed along with the deformation of laminated rubber to absorb the seismic energy, quickly damps the vibration, and controls the displacement due to the earthquake as well.
- 5. Depresses the vibration other than the earthquake (Trigger function)
High rigidity of the lead plug will hold the structure until the external force becomes as high as a certain level to prevent the vibration due to the traffic vibration or the strong wind.
The Durability of Rubber Bearing
The elevated railway bridge in Australia (Melbourne) built in 1889 using the natural rubber (single layer) for a countermeasure to the vibration/noise is considered as the oldest still existing practical example of rubber bearing for the bridge in the world.
As a full-fledged application of laminated rubber bearing, the use for Pelham Bridge (steel bridge) in UK (Lincoln City) is considered as the first practical example. After that, the laminated rubber has been a share of bridge bearing until today.
On the other hand, the oldest example in Japan is the chloroprene laminated rubber bearing used for Kinugawa Bridge for Tohoku Main Line in 1961, and this bearing is still in use with no problem over 40 years after installation.

Elevated Railway Bridge (Melbourne) Installed in 1889

Kinugawa Bridge Installed in 1961
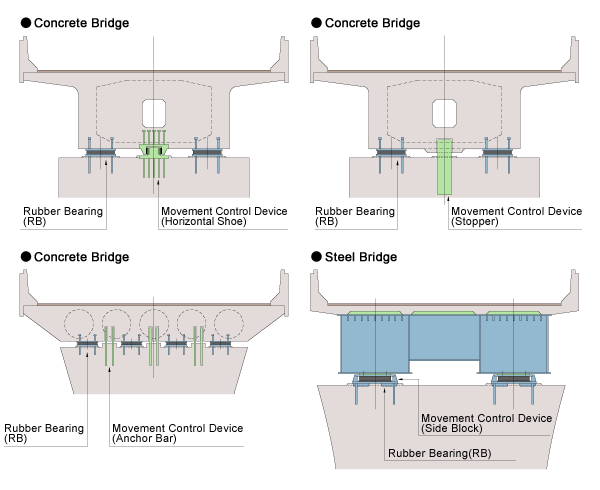
Examples of Installation
LRB can be applied to the wide variety of bridges, such as concrete bridges and steel bridges.
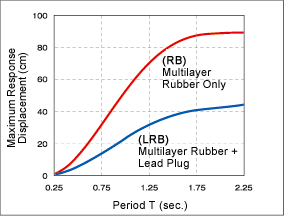
Basic Characteristics Verification Test
A great number of basic experiments and confirmation of property are being made to prove the performance of rubber bearings.



