This website uses cookies for a better browsing experience.
If you agree to the use of cookies, please click the "Agree" button.
Please refer to the Privacy Policy regarding the use of cookies on this site.
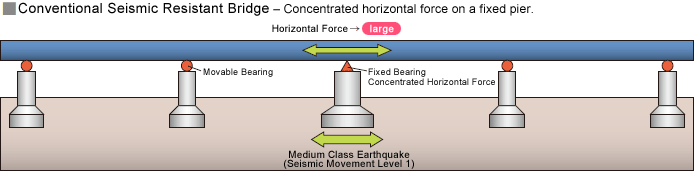
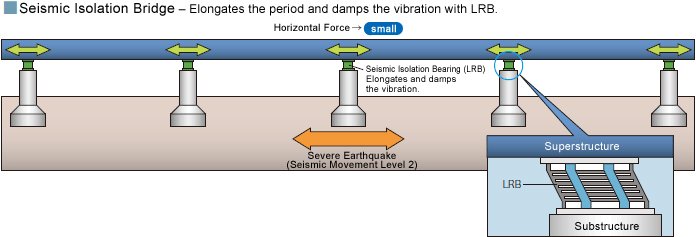
The sufficient earthquake safety is strongly requested in Japan, a world’s premier earthquake country. The traditional bridges have been adopting the seismic resistant design, which endures the earthquake with the strength of the bridge member. Recently those bridge types have been adopted, such as the load dispersion bridge, which disperses the inertial force of superstructure to protect the bridge from the earthquake; the seismic isolation bridge that uses the seismic isolation bearing to support the superstructure to survive the earthquake with the elongated period of seismic movement and damping effect to cope with the Great Kanto Earthquake class severe earthquakes; or the vibration control bridge, which controls the response displacement and the load sharing among the bridge piers.
Seismic Isolation Bridge and Load Dispersion Bridge
Seismic Isolation Bridge
The bridge type that survives the earthquake by the elongated period of seismic movement and damping effect, supporting the beams using the seismic isolation bearing to cope with the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake class earthquakes.
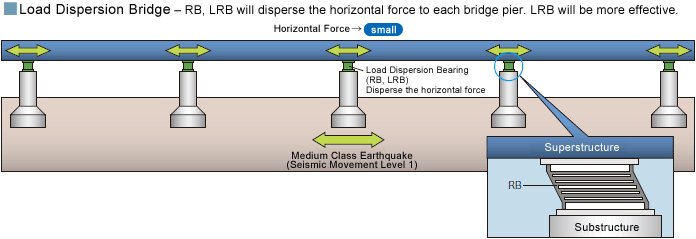
Mechanism of Load Dispersion Bridge
The load dispersion bridge is presented to cope with the earthquake by dispersing the inertial force of superstructure utilizing the multipoint elastic supporting rubber bearings for the superstructure.
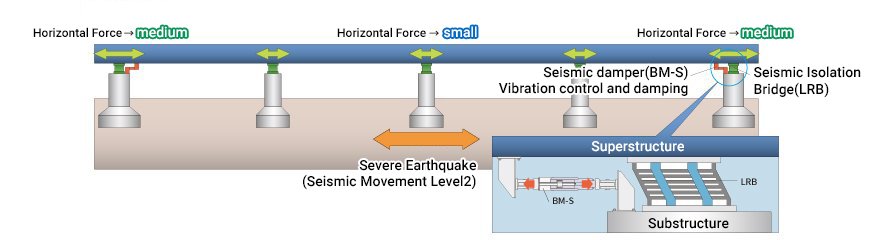
Load Dispersion Bridge
The load dispersion bridge is presented that copes with the earthquake by dispersing the inertial force of superstructure utilizing the multi-point elastic supporting rubber bearings for the superstructure.
(Reference) Conventional bridges